

If noncollinearity exists between two members meeting at a joint that is not subjected to any external force, then the two members are zero force members (see Figure 5.11a).Ģ. The truss-member arrangements that result in zero force members are listed as follows:ġ. Sometimes, such members are introduced into the truss system to prevent the buckling and vibration of other members. If this initial assumption is incorrect, the computed values of the axial forces will be negative, signifying compression.Īfter completing the analysis of joint A, joint B or D can be analyzed, as there are only two unknown forces.Ĭomplex truss analysis can be greatly simplified by first identifying the “zero force members.” A zero force member is one that is not subjected to any axial load. The two unknown forces are initially assumed to be tensile (i.e. By applying the equations of static equilibrium to the free-body diagram shown in Figure 5.10b, the support reactions can be determined as follows: Figure 5.10c. Using the method of joint, determine the axial force in each member of the truss shown in Figure 5.10a. The detailed procedure for analysis by this method is stated below.

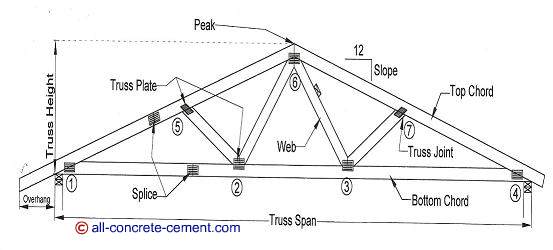
The method of joint involves successively isolating each joint in a truss system and determining the axial forces in the members meeting at the joint by applying the equations of equilibrium. This method is based on the principle that if a structural system constitutes a body in equilibrium, then any joint in that system is also in equilibrium and, thus, can be isolated from the entire system and analyzed using the conditions of equilibrium. In truss analysis, a negative member axial force implies that the member or the joints at both ends of the member are in compression, while a positive member axial force indicates that the member or the joints at both ends of the member are in tension.ĥ.6.2 Analysis of Trusses by Method of Joint There are several methods of truss analysis, but the two most common are the method of joint and the method of section (or moment). Joint identification ( a) and bar force ( b).Ĭlassify the trusses shown in Figure 5.5 through Figure 5.9 as stable, determinate, or indeterminate, and state the degree of indeterminacy when necessary. For example, the member force F AB in the truss shown in Figure 5.4 is the force in the member connecting joints A and B. A bar force can be represented by any letter ( F or N or S), with two subscripts designating the member. However, consistency must be maintained in the chosen way of identification to avoid confusion during analysis. Truss joints can be identified using alphabets or numbers, depending on the preference of the analyst. Loads are applied only at the joints due to the arrangement of members.ĥ.5 Joint Identification and Member Force Notation Members’ deformation under loads are negligible and of insignificant magnitude to cause appreciable changes in the geometry of the structure.Ĥ. Members are straight and, therefore, are subjected only to axial forces.ģ.

Members are connected at their ends by frictionless pins.Ģ. The conditions of determinacy, indeterminacy, and instability of trusses can be stated as follows:ġ. The following are examples of different types of trusses for bridges and roofs. A complex truss is neither simple nor compound, as shown in Figure 5.1c its analysis is more rigorous than those of the previously stated trusses. A compound truss consists of two or more simple trusses joined together, as shown in Figure 5.1b. Additional joints can be formed in the truss by subsequently adding two members at a time to the base cell, as shown in Figure 5.1a. A simple truss is one constructed by first arranging three slender members to form a base triangular cell. A truss can be categorized as simple, compound, or complex. \)Ī truss is a structure composed of straight, slender members connected at their ends by frictionless pins or hinges.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
